WHAT IS A PRESSURE DECAY LEAK TEST?
Pressure Decay Leak Testing is a critical method for detecting leaks in various industries. This process involves filling a test part with air or gas, isolating it, and measuring the pressure drop over a certain period of time. Significant pressure drops indicate leaks, making this method essential for ensuring product integrity. This method is valued for its sensitivity and versatility across various industries, including automotive, medical devices, and consumer electronics.
BENEFITS OF USING PRESSURE DECAY LEAK TESTING
- High Sensitivity
- Capable of detecting small leaks, ensuring product integrity
Versality
- Suitable for both pressure and vacuum testing environments
- Quantifiable Results
- Provides precise leak rate measurements
- Simplicity
- Easy integration into automated lines
Cost-Effective
- Low maintenance and operational costs
DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE DECAY SENSORS
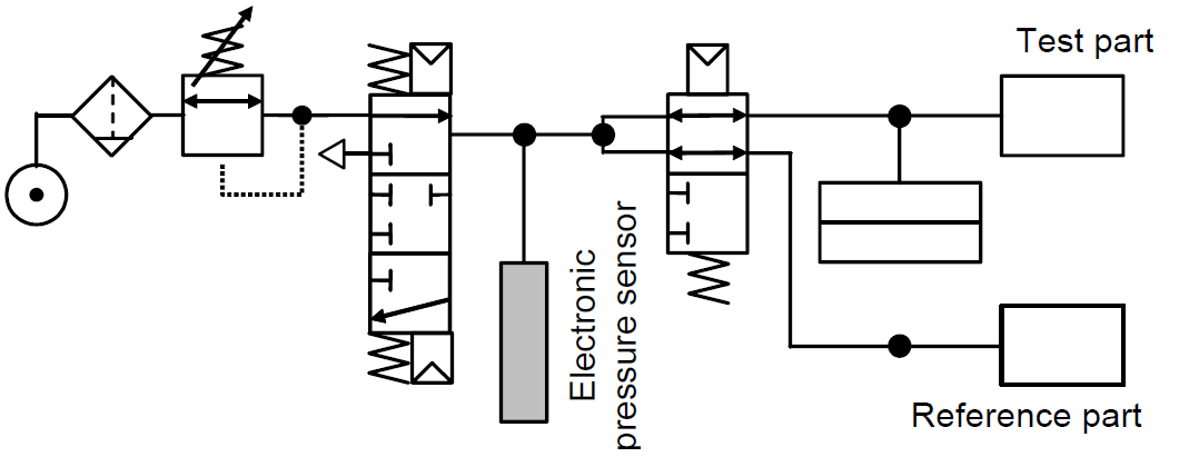
Uses two pressure sensors, one to measure the test pressure and a second to measure the differential pressure drop from a leak. Differential sensors are different solution to leak test components. These sensors use a reference part alongside the test part to compare pressure drops. By measuring the differential pressure between two volumes (reference part & test part), they reduce the impact of environmental factors. This method enhances reliability and sensitivity, making it ideal for stringent control applications. Although more complex and expensive, differential measurement sensors provide improved accuracy and are essential for critical testing scenarios where precision is paramount.
Direct Measurement Principle
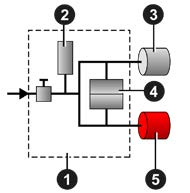
Figure 1

Direct Measurement: The part under test 3 and the reference part 5 are filled to an identical pressure. A differential sensor 4 measures the pressure variation between the part under test 3 and the reference part 5. In some applications, the reference part can be replaced by a cap.
- Device
- Pressure Sensor
- Part Under Test
- Differential Pressure Sensor
- Reference Part
Case Study 1
No Leak
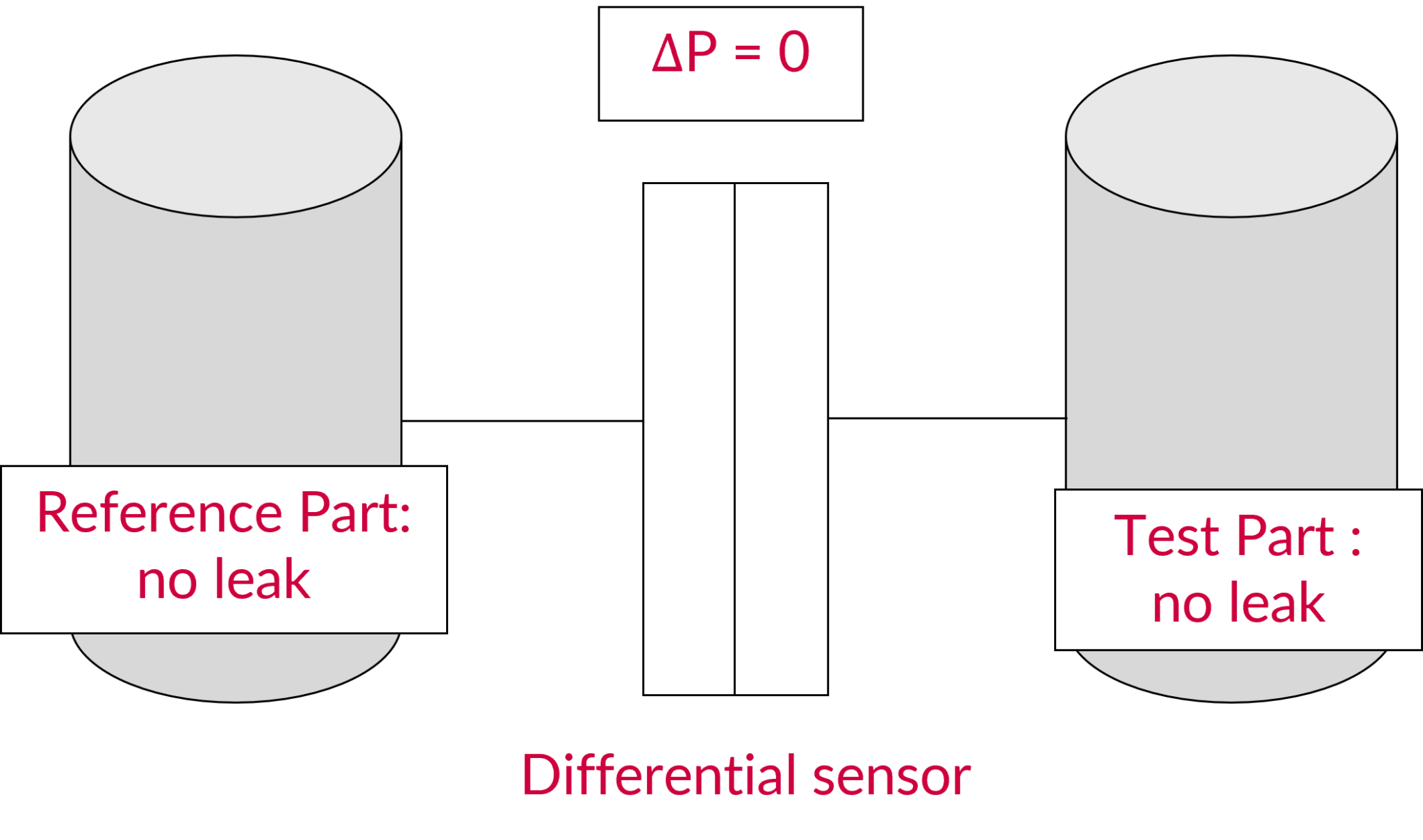
In the case where there is no leak in your test part and your reference part, Delta P=0.
Case Study 2
Leak in the Test Part
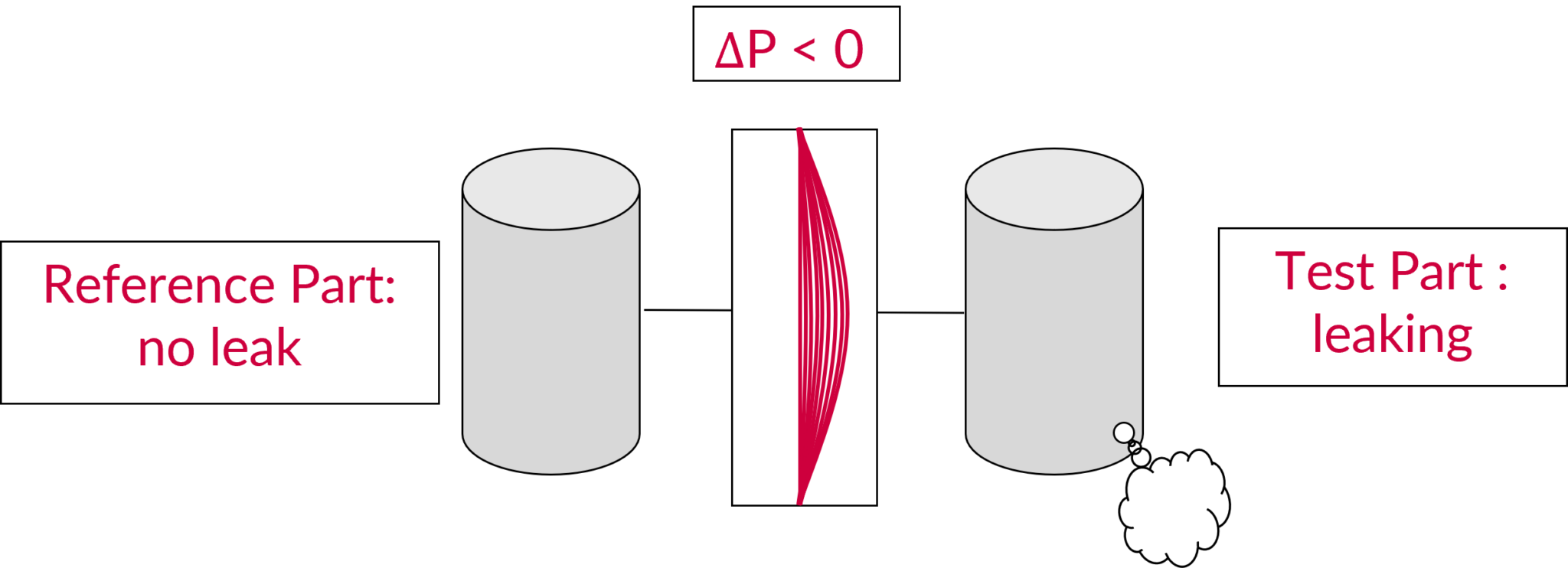
In the case where there is a leak in your test part and not in the reference part, Delta P will be positive (greater than 0).
Case Study 3
Leak in the Reference Part
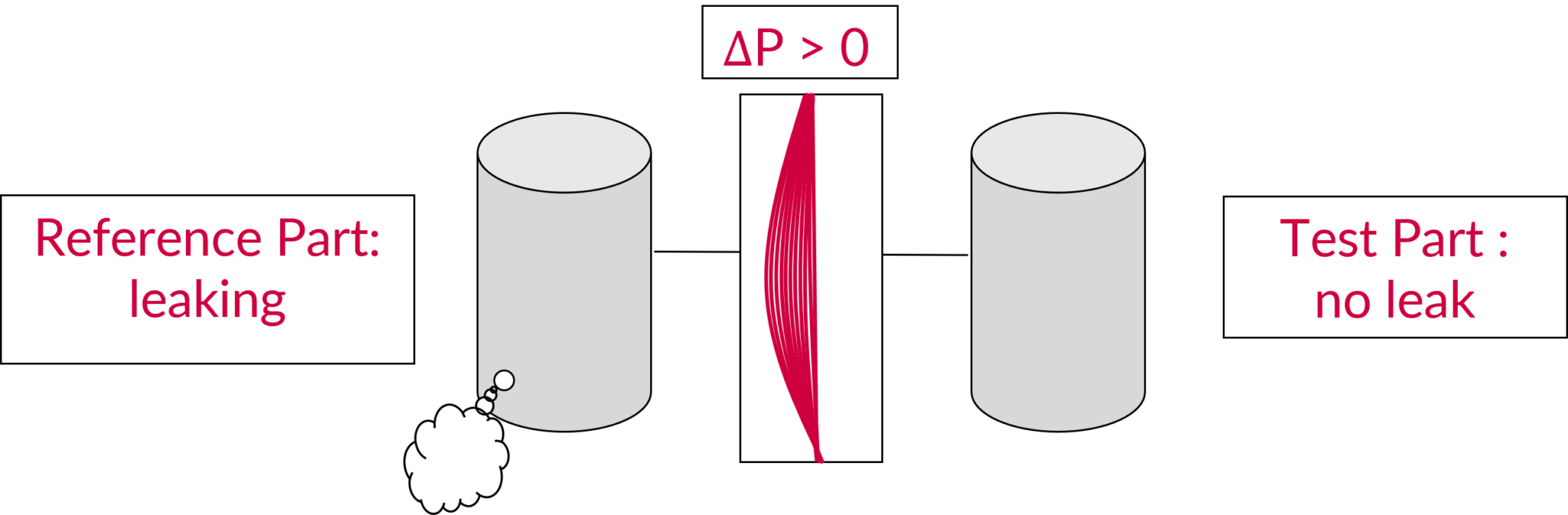
In the case where there is a leak in your reference part and not in the test part, Delta P will be negative.
APPLICATION EXAMPLES USING PRESSURE DECAY LEAK TEST
- A/C Systems
- Exhaust Systems
- Gearbox
- Fuel & Brake Lines
- Reservoir Tanks…
- Bottle Cap
- Cosmetic Packaging
- Food Packaging
- Plastic Bottles
- Ink Cartridges
- Smartphones
- Smartwatches
- Speakers
- Drones
- Cameras…
DIRECT PRESSURE DECAY TEST
In a direct leak test using the differential pressure decay method, both the test part and a reference part are filled to the required pressure level. The instrument then measures the differential pressure between these two volumes, which are separated by an equalization valve. The test pressure is directly applied to the test parts.
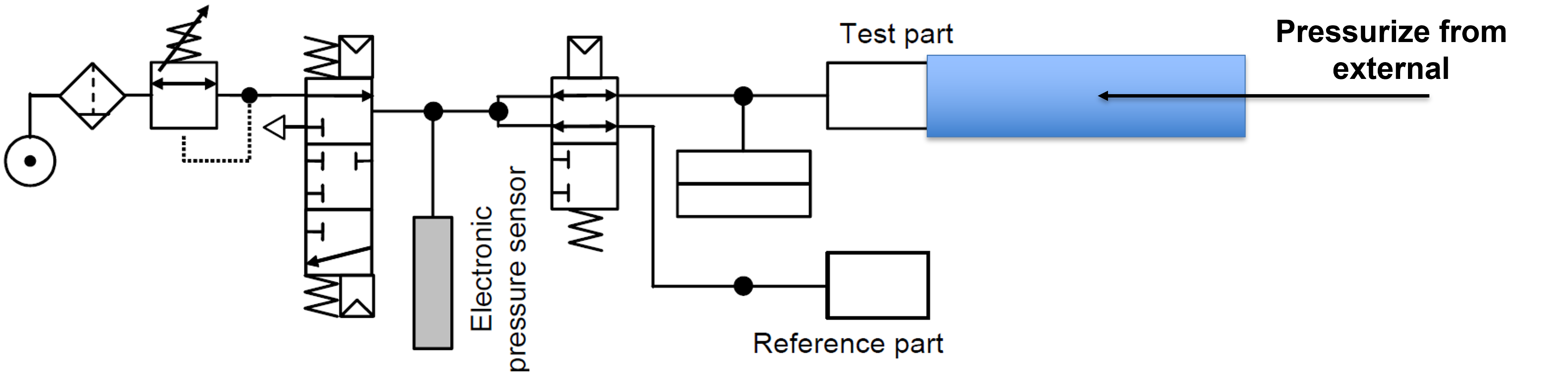
INDIRECT PRESSURE DECAY TEST
In an indirect leak test, the test part is placed in a sealed bell, which is pneumatically connected to the instrument. The part is externally pressurized, with pressures reaching up to 200 bar, while the bell is lightly pressurized. If there is a leak in the test part, the pressure inside the bell will rise. This method allows for the detection of leaks by monitoring the pressure increase in the bell, providing a reliable and effective means of identifying leaks in high-pressure application. The Indirect Method will improve the cycle time.
RELATIVE PRESSURE DECAY SENSOR
Uses one sensor to measure the pressure drop in the test part without using a reference volume. Relative measurements sensors are essential for accurate pressure decay testing, especially for basic applications. While this method is straightforward and cost-effective, it is more susceptible to environmental fluctuations. This can affect the accuracy of the test results. Despite these challenges, relation measurement remain a popular choice due to the simplicity and ease integration into various leak testing systems.
The test pressure is applied at the entrance of the test part 3, and the measurement is performed by the pressure sensor 2.
- Device
- Pressure Sensor
- Test Part
Relative Measurement Principle
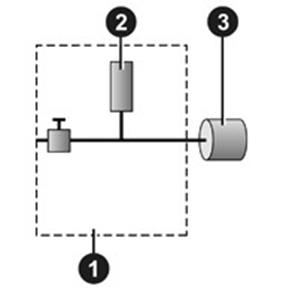
Figure 1




